【Situation Requirements and Policy Priorities for Carbon Reduction of Road Transportation in China】
(同济大学中国交通研究院,上海 200092)
近年来,我国公路交通行业高度重视“碳达峰”“碳中和”,尽快实现“双碳”目标是行业关注的焦点问题。为此,本刊特邀相关专家从政策制定到工程实践等方面,介绍推动行业绿色低碳发展的新技术、新模式、新业态。
2030年前实现“碳达峰”、2060年前实现“碳中和”是中国向世界承诺的气候雄心。交通运输作为与工业、能源并列的三大主要碳排放行业之一,统筹推进零碳转型与支撑经济增长的任务十分艰巨。其中,公路交通既是运输量最大的运输方式,也是交通运输领域最主要的碳排放来源,成为能否实现“30·60”愿景目标的重中之重。现有各类政策规划对于公路交通减碳做了系统部署,重点针对推动运输结构调整、推动设备升级、推广清洁能源、推动科技创新、完善监测体系等主要举措的多个方面。落实《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》《交通强国建设纲要》等重大战略政策要求,支撑国家现代化建设,建议可从战略性减碳、技术性减碳和管理性减碳三大领域实化顶层设计和工作举措,早日实现公路交通“碳达峰”和“碳中和”。
一、我国公路交通减碳发展的形势要求
(一)交通运输是全球碳排放的主要来源根据国际能源署、我们的数据世界(Our World in Data)等机构数据[1,2],截至2021年底,全球石化能源消耗产生的二氧化碳排放总量超过370亿吨,已超过2019年新冠疫情暴发前的水平,再创历史新高。分国别来看,由于我国仍处于快速发展阶段,是全球碳排放总量最大的国家,约为115亿吨,占全球碳排放量的21%;分部门来看,来自交通运输部门能源消耗的碳排放约占全球碳排放的16.2%~25%,与工业、建筑并列为碳排放的三大主要来源。就我国的碳排放来源构成来看,来自我国交通运输部门的碳排放量约在10亿吨左右,根据不同计算来源[3~5],约占我国碳排放总量的7.6%~11%,位于建筑制造、电力和工业之后,仍是碳排放的主要来源之一。
(二)公路交通是我国交通碳排放的最大来源
分运输方式来看,公路交通既是运输量最大的运输方式,也是全球碳排放总量最大的运输方式,来自公路交通的碳排放约占全球碳排放量的11.9%。就我国的交通运输碳排放构成来看,来自公路交通的碳排放量占国内交通运输碳排放的比重超过80%,远高于公路交通完成的客货运输量占比。因此,促进公路交通部门减少碳排放成为我国落实“双碳”战略的主要任务之一。
在公路运输各种车型中,各类货车的碳排放量占所有公路运输车辆排放的比重达到60%,尤其是重型货车的排放量最大,占公路运输碳排放总量的比重超过50%,其他类型车辆碳排放占比均不超过6%。重型货车是未来我国公路交通及整个交通运输领域减排的重中之重。
二、我国公路交通减碳发展的政策重点
(一)公路交通减碳发展的主要政策
1.国家层面
《交通强国建设纲要》《国家综合立体交通网规划纲要》均提出“我国到2035年基本建成交通强国”,并将绿色交通作为主要发展目标和重要建设内容,提出“打造绿色高效的现代物流系统”“强化节能减排和污染防治”等战略任务。国务院印发《2030年前碳达峰行动方案》,将“交通运输绿色低碳行动”作为十大行动之一,要求加快形成绿色低碳运输方式,确保交通运输领域碳排放增长保持在合理区间,并提出“陆路交通运输石油消费力争2030年前达到峰值”“‘十四五’期间,集装箱铁水联运量年均增长15%以上”等具体目标。
国务院办公厅印发《推进多式联运发展优化调整运输结构工作方案》,提出以发展多式联运为抓手,推动各种交通运输方式深度融合,进一步优化调整运输结构,基本形成大宗货物及集装箱中长距离运输以铁路和水路为主的发展格局,全国铁路和水路货运量比2020年分别增长10%和12%。《“十四五”现代综合交通运输体系发展规划》提出,全面推动交通运输全生命周期绿色低碳转型,交通运输二氧化碳排放强度下降5%。此外,《中共中央国务院关于深入打好污染防治攻坚战的意见》《中共中央国务院关于完整准确全面贯彻新发展理念做好碳达峰碳中和工作的意见》《国家综合立体网规划纲要》等国家政策文件,对公路交通节能减排提出了具体要求和行动部署。
2.部委层面
《公路“十四五”发展规划》要求贯彻落实绿色发展理念,推动公路交通与生态保护协同发展,继续深化绿色公路建设,促进资源能源节约集约利用,加强公路交通运输领域节能减排和污染防治,全面提升公路行业绿色发展水平。《绿色交通“十四五”发展规划》要求协同推进交通运输高质量发展和生态环境高水平保护,并提出建设绿色交通基础设施、优化交通运输结构、推广应用新能源、推进交通污染深度治理、强化绿色交通科技支撑、完善绿色交通监管体系、深化国际交流与合作等7项重点任务。《综合运输服务“十四五”发展规划》要求打造清洁低碳的绿色运输服务体系,并提出建立低碳转型政策体系、深入开展绿色出行行动、深入推进城市绿色货运配送示范创建、大力发展清洁化运输装备等主要任务。
3.省市层面
各省市也通过综合交通“十四五”规划、绿色低碳交通规划、交通强国建设试点等方式落实,推进公路交通减碳发展。根据公开资料,29个省份的《“十四五”综合交通运输规划》均有公路交通绿色发展的部署,另外还有6个省份已公开发布《绿色交通“十四五”规划》、两个省份已公开发布《交通运输节能环保“十四五”发展规划》、12个省份已公开发布《新能源汽车产业发展“十四五”规划》、24个省份已公开发布《碳达峰碳中和“1+N”》政策文件。湖北、江西等6个省份设置了交通运输二氧化碳排放强度下降率目标,广西、天津、吉林等17个省份设置了营运车辆单位运输周转量二氧化碳排放下降率目标,浙江、广东、北京等14个省份设置了中心城区绿色交通出行比例目标[6]。
(二)公路交通减碳发展的政策重点
公路交通是我国能源消费和温室气体排放的主要部门,成为落实“双碳”战略的重点领域。欧美国家经验表明交通部门碳达峰晚于工业、住宅和商业等部门,因此也是“脱碳”难度最高的行业。梳理国家和省市关于公路交通减碳的具体部署,政策重点包括推动运输结构调整、推动设备升级、推广清洁能源、推动科技创新、完善监测体系等主要举措。
1.调整运输结构
政策要点在于通过大力发展多式联运,推动不同运输方式合理分工、有效衔接,降低空载率和不合理客货运周转量。政策重点包括发挥铁路和水路的低碳优势,完善骨干通道和集疏运体系,推动铁路场站向重点港口、枢纽机场、产业集聚区、大宗物资主产区延伸;创新多式联运组织,大力发展内贸多式联运和集约化配送,推动冷链、危化品、国内邮件快件等专业化联运发展;促进重点区域运输结构调整,京津冀及周边地区、长三角地区、粤港澳大湾区等沿海主要港口,利用疏港铁路、水路、封闭式皮带廊道、新能源汽车运输大宗货物的比例力争达到80%。
2.升级设施装备
政策要点在于推广绿色化、轻量化、环保型交通装备及成套技术装备,加速淘汰落后技术和高耗低效交通装备,降低营运公路交通工具碳排放强度。政策重点包括推进运输装备标准化,推广跨方式快速换装转运标准化设施设备,降低空箱调转比例,提高装卸和转运效率;提高资源再利用和循环利用水平,推广施工材料、废旧材料再生和综合利用。
3.推广清洁能源
政策要点在于通过扩大新能源、清洁能源在交通运输领域应用,逐步降低传统燃油在能源消耗中的占比。政策重点包括在公路沿线合理布局光伏发电及储能设施,有序推进充电桩、配套电网、加注(气)站、加氢站等基础设施建设等具体举措。
4.推动科技创新
政策要点在于探明公路交通与节能减排的作用机理,突破绿色低碳交通重大关键技术,通过技术创新与推广应用挖掘节能减排的更大潜力。政策重点包括深化交通污染综合防治等基础理论研究,研发交通能耗与污染排放监测监管等新技术;强化加快节能环保关键技术推广应用,强化新能源运输装备和设施设备、氢燃料动力车辆、绿色建筑材料工艺等新装备研发;健全绿色交通标准规范体系,强化节能降碳限制准入标准、绿色运行规范、污染排放限值标准等标准的制定。
5.完善监测体系
政策要点在于完善碳排放监测体系和控制政策,弥补关于碳排放测算领域的空白,形成公路交通碳排放管理闭环。政策重点包括加强碳排放基础统计核算,研究制定交通运输领域碳排放统计方法和核算规则;强化绿色低碳交通激励约束机制,分类完善信用交通、碳积分、合同能源管理、碳排放核查、绿色金融等新型治理措施;利用在线监测系统及大数据技术,建立交通运输碳排放监测平台系统,推动近零碳交通示范区建设等具体举措。
三、“双碳”战略下的我国公路交通发展趋势
借鉴国内外典型做法和发展经验,本文建议可从战略性减碳、技术性减碳和管理性减碳三大领域,持续优化顶层方案设计和工作举措,形成中国式“零碳”公路交通可持续发展模式。
(一)实化战略性减碳举措
战略性减碳举措主要针对公路交通碳减排的顶层战略,提出整体战略布局、政策体系和标准规划,具体举措主要包括制定公路交通运输碳排放测算方法和标准规范,形成清晰化、透明化的排放数据和指标体系,明确基准场景和基准年份的公路交通碳排放总量及其现状构成;出台“公路交通运输业30·60行动路线图”,以“碳强度”控制为主、碳排放总量控制为辅,明确公路交通减碳的主要领域、实现方式和阶段性目标,进一步凝聚减碳共识和合力;深化与欧盟国家在交通减碳领域的交流,在交通碳排放定价和交易体系、碳排放标准互认与数据共享、跨境基础设施互联互通、零碳机场和零碳港口共建、清洁能源区域联盟等方面深化合作。
(二)加大技术性减碳投入技术性减碳举措主要针对技术
进步和可科技创新领域,提出公路交通碳减排新技术、新方法和新模式,具体举措主要包括建立公路交通运输碳排放统计监测平台,运用大数据、物联网、区块链等数字技术,实现分方式、分企业、分区域碳排放精细化管理;大力发掘交通新技术的减碳空间,如卡车编队行驶可降低碳排放10%~15%,应大力发展自动驾驶、编队行驶、光伏路面、电气化公路、地下物流、出行即服务(MaaS)等新模式。
(三)创新管理性减碳举措
管理性减碳举措主要针对管理体系和治理能力方面,提出公路交通碳减排的奖惩机制制度,具体举措主要包括建立低碳交通认证制度,完善相关标准和认证流程,只有经过低碳交通认证的交通企业、工程或者项目,才能申请交通部门的相关优惠政策,并实行“高碳排放一票否决制”;创新绿色交通融资制度,通过发行绿色交通债券、降低绿色交通项目资本金、延长经营性项目收费年限等措施,加大对于绿色交通基础设施的投资力度;开展零碳交通能力建设,组织大型交通和物流企业形成零碳联盟,发起脱碳减碳倡议,并广泛开展培训、技术交流、理念推广等能力建设工作;推广交通运输碳排放交易体系,按照“污染者付费”原则,实施碳排放定价、排放收费、碳汇补贴等举措,建立零排放区域,完善交通行业碳排放交易市场。
参考文献
1.Our World in Data. Global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels. https://ourworldindata.
org/co2-emissions
2.Pierre Friedlingstein et al. Global Carbon Budget 2022, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 14,4811–4900,https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-4811-2022, 2022.
3.甄敬怡.“双碳”目标下交通运输如何当好“开路先锋”[N].中国经济导报, 2022-07-02(002). DOI:10.28095/n.cnki.ncjjd.2022.000925.
4.陆化普,冯海霞.交通领域实现碳中和的分析与思考[J].可持续发展经济导刊, 2022(Z1):63-67.
5.黄黎晨,曹乔松.碳中和目标下交通领域绿色发展对策分析[J].城市交通,2021,19(05):36-42.DOI:10.13813/j.cn11-5141/u.2021.0503.
6.韩迪.双碳行动看行业系列报告:各省“十四五”交通领域绿色低碳行动力度观察[R].北京:绿色创新发展中心,2022.
Focused on “Dual Carbon”(First Chapter)
In recent years, Chinese highway transport industry has attached great importance to Carbon peak and carbon neutrality, and realizing the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals has been the focus of the whole industry. To this end, we invite relevant experts to introduce new technologies, new models and new business forms that promote the green and low-carbon development of the industry from the aspects of policy formulation to engineering practice.
Situation Requirements and Policy Priorities for Carbon Reduction of Road Transportation in China
Tan Lin
(China Transportation Institute at Tongji University,Shanghai 200092)
It is the climate ambition of China committed to the world, to achieve “carbon emission peak” by 2030 and “carbon emission neutrality” by 2060. Transportation, as one of the three major carbon emission industries along with industry and buildings, is confronted with difficult dual task of promoting the zero carbon transformation as well as supporting economic growth comprehensively. Road Transportation in particular, which is not only the transportation mode with the most volume, but also the transportation mode with the most carbon emissions, is becoming the top priority of achieving the “2030·2060” vision goal. Systematic deployment for road transportation carbon reduction has been made by various existing policy and plans, focusing on transportation structure adjustment, equipment upgrading, clean energy promotion, scientific and technological innovation, monitoring system improvement and other major initiatives. In order to implement the major strategic policies such as “The Action Plan for Achieving the Carbon Peak by 2030” and “The Outline for Building a Transportation Powerful Country”, and to support national modernization, it is suggested that further top-level policy priorities can be implemented in three major areas, namely, strategic carbon reduction initiative, technical carbon reduction initiative and managerial carbon reduction initiative.
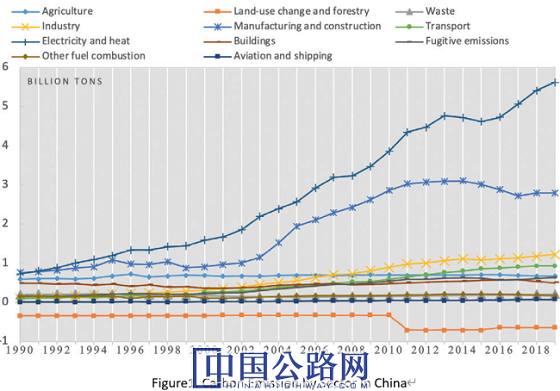
1. Requirements for Carbon Reduction of Road Transportation in China
1.1 Transportation as the main source of global carbon emissions
According to data from International Energy Agency, Our World in Data and other institutions [1,2], the total carbon dioxide emissions generated by global petrochemical energy consumption will be more than 37 billion tons by the end of 2021, which has exceeded the level before the outbreak of the COVID-19 in 2019. From the perspective of different countries, China is the largest country of carbon emissions with about 11.5 billion tons currently, accounting for about 21% of the global carbon emissions. From the perspective of different sectors, the transportation sector accounts for about 16.2%~25% of global carbon emissions, which is one of the three major sector sources of carbon emissions, along with industry and buildings. The transportation sector in China emits about 1 billion tons of carbon roughly. According to different calculation method [3~5], the transportation sector accounts for 7.6%~11% of China's total carbon emissions, which is still one of the main sources of carbon emissions, ranking after manufacturing and construction, power and industry.
1.2 Road as the largest source of transportation carbon emissions in China
From the perspective of transportation modes, road transportation is not only the transportation mode with the most volume, but also the mode with the largest share of global transportation carbon emissions. The carbon emissions from road transportation account for about 11.9% of the global carbon emissions. As to the case in China, road transportation accounts for more than 80% of domestic transportation carbon emissions, which is far higher than the proportion of passenger and freight volume transported. Therefore, it is one of the main tasks for China to promote road transportation carbon emission reduction, so as to achieve the “Double Carbon” strategy.
1.3 Road freight as the top priority of road transportation carbon reduction in China
Among all types of road transportation vehicles, trucks account for 60% of the road transportation emissions. Especially, heavy trucks account for more than 50% of the total road transportation carbon emissions. In contrast, the carbon emissions of any other types of vehicles do not exceed 6%. In 2020, China has more than 270 million civil vehicles, including 30.4 million trucks as well as 8.4 million heavy trucks. Trucks and heavy trucks will account for 11.1% and 3.1% of the total civil vehicles respectively. The proportion of heavy truck emissions in road transportation far exceeds the proportion of its vehicles. Thus, heavy trucks will be the top priority of carbon emission road transportation and the entire transportation field in China in the future.
2. Policy Focus of China's Road Transportation Carbon Reduction Development
2.1 Main policies for carbon reduction development of road transportation
2.1.1 National level
Both “The Outline for the Construction of a Transportation Powerful Country” and “The Outline for the Planning of the National Comprehensive ThreeDimensional Transportation Network” present the aim of a strong transportation country by 2035, and propose strategic tasks such as “building a green and efficient modern logistics system” and “strengthening energy conservation, emission reduction and pollution prevention”. The State Council issued “The Action Plan for Achieving the Carbon Peak by 2030”, which takes the “Green and Low Carbon Action in Transportation” as one of the top ten actions, calling for accelerating the formation of green and low carbon transportation system, ensuring the growth of transportation carbon emissions within a reasonable range, and putting forward specific goals such as “striving to reach the peak of oil consumption in land transportation by 2030” “the average annual growth of container rail-water intermodal transportation will be more than 15% in the 14th Five Year Plan period”. “The Work Plan for Promoting the Development of Intermodal Transportation and Optimizing the Transportation Structure” issued by The General Office of the State Council, proposes to take the development of intermodal transportation as the starting point, to promote the deep integration of various transportation modes and further optimization of transportation structure adjustment. It aims to form a development pattern of bulk cargo and container medium and long-distance transportation dominated by railways and waterways basically. The national railway and waterway freight volume should be increased by about 10% and 12% respectively, compared with 2020. “The 14th Five Year Plan for the Development of Modern Comprehensive Transportation System” proposes to comprehensively promote the green and low-carbon transformation of transportation throughout its life cycle, and reduces the carbon dioxide emission intensity of transportation by 5%. In addition, such national policies as “The Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Deepening the Pollution Prevention and Control Campaign”, “The Opinions of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on Completely, Accurately and Comprehensively Implementing the New Development Concept and Carbon Peak & Carbon Neutralization Strategy”, “The New Energy Industry Development Plan (2021-2035)”, put forward specific requirements and action plans for road transportation energy conservation and emission reduction as well.
2.1.2 Sectoral level
“The 14th Five Year Plan for Highway Development” requires the implementation of the principle of green development, by promoting the coordinated development of highway transportation and ecological protection, deepening the construction of green highways, promoting the conservation and intensive use of resources and energy, strengthening energy conservation and emission reduction and pollution prevention in the field of highway transportation, and improving the green development level of the highway industry comprehensively. “The 14th Five Year Plan for the Development of Green Transportation” calls for coordinated promotion of high-quality development of transportation and high-level protection of the ecological environment by proposing seven key tasks, including building green transportation infrastructure, optimizing transportation structure, promoting the application of new energy, promoting in-depth treatment of transportation pollution, strengthening green transportation science and technology support, improving the green transportation regulatory system, and deepening international exchanges and cooperation. “The 14th Five Year Plan for the Development of Comprehensive Transportation Services” requires the establishment of a clean and low-carbon green transportation service system, and puts forward the main tasks of establishing a low-carbon transformation policy system, carrying out green travel action in depth, promoting the demonstration of urban green freight distribution, and vigorously developing clean transportation equipment. In addition, policies such as “The Action Plan for Diesel Truck Pollution Control”, “The 14th Five Year Plan for Modern Circulation System”, “The Green Transportation Standard System (2022)” and “The Notice on the Establishment and Implementation of a Vehicle Emission Inspection and Maintenance System”, put forward specific requirements and action plans for road transportation energy conservation and emission reduction as well. The transportation departments also actively adopted the intermodal transportation demonstration project, the establishment of national transit metropolis, the establishment of green freight distribution demonstration cities, green travel action plans and other specific actions, to promote low-carbon development of road transportation.
2.1.3 Local level
Most provinces and cities promote the development of local transportation carbon reduction actively, through comprehensive transportation “14th Five Year Plan”, green and low-carbon transportation planning, and pilot construction of transportation powerful country. According to the public information, the “14th Five Year Plan” Comprehensive Transportation Plans of 29 provinces has the deployment of green development of road transportation. In addition, 6 provinces have released the “14th Five Year Special Plan” for green transportation, 2 provinces have released the “14th Five Year Special Plan” for energy conservation and environmental protection in transportation, 12 provinces have released the “14th Five Year Special Plan” for the development of new energy automobile industry. 6 provinces, including Hubei, Jiangxi, have set targets for the reduction rate of carbon dioxide emission intensity of transportation. 17 provinces, including Guangxi, Tianjin and Jilin, have set targets for the reduction rate of carbon dioxide emission per unit transportation turnover of operating vehicles. 14 provinces and cities, including Zhejiang, Guangdong and Beijing, have set targets for the proportion of green transportation trips in central urban areas [6].
2.2 Policy Priorities of Road Transportation Carbon Reduction Development
Road transportation is the main sector of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in China, so it has become the key area to implement the “Double Carbon” strategy. European and American experience shows that the carbon emission peak of transportation sector is later than that of industrial, residential and commercial sectors, which marks the transportation industry with the highest difficulty in decarbonization. After sorting out the specific national, provincial and municipal plans for carbon reduction in road transportation, it is clear that the policies focus on promoting transportation structure adjustment, promoting equipment upgrading, promoting clean energy, promoting scientific and technological innovation, improving the monitoring system and other major initiatives.
2.2.1 Adjusting transportation structure
The key point of this policy is to promote the rational division and effective connection of different transportation modes by vigorously developing intermodal transportation, and reducing the no-load rate and unreasonable passenger and freight turnover. Policy priorities include giving full play to the low carbon advantages of railways and waterways, improving backbone channels and collection and distribution systems, and promoting the extension of railway stations to key ports, hub airports, industrial clusters, and major bulk material production areas; innovating intermodal transportation organization, vigorously developing domestic trade intermodal transportation and intensive distribution, and promoting the development of cold chain, dangerous chemicals, domestic mail express and other specialized freight transportation; accelerating the transfer of bulk goods and medium and long distance goods from road transportation to railway and waterway transportation, the proportion to railway transportation of coal and coke should strive to reach 90% in the main coal producing areas of Shanxi, Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia (with the transportation distance of more than 500 kilometers); promoting the adjustment of transportation structure in key regions, and bulk goods transportation strive to reach 80% by railway, waterway, closed belt corridor and new energy vehicles of major coastal ports such as Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and surrounding regions, the Yangtze River Delta, the Greater Guangdong-Hong KongMacao Bay Area; promoting the green travel system, and building a public transportation travel system with urban rail transit and bus rapid transit system as the backbone and conventional bus as the main body.
2.2.2 Upgrading facilities and equipment
The key point of this policy is to promote green, lightweight and environment-friendly transportation equipment and complete sets of technical equipment, to accelerate the elimination of high pollution and low-efficiency transportation equipment, and reduce the carbon emission intensity of road transportation vehicles. Policy priorities include controlling diesel truck pollution, accelerating the promotion and application of operating vehicles with the newest emission standards; establishing the closed-loop management mechanism of vehicle emissions, and accelerating the kickout of old vehicles with high energy consumption and high emissions; promoting the standardization of transportation equipment, promoting the standardized facilities and equipment for cross mode rapid transshipment, reducing the proportion of empty container transshipment, and improving the efficiency of loading, unloading and transshipment; improving the reuse and recycling level of resource, promoting the recycling and comprehensive utilization of construction materials and waste materials, and promoting the greening and reduction of express packaging.
2.2.3. Promoting clean energy
The key point of this policy is to reduce the proportion of fossil fuel in energy consumption gradually by expanding the application of new energy and clean energy in the field of transportation. Policy priorities include: vigorously promoting new energy vehicles, promoting the electrification of urban public service vehicles, and promoting electric power, hydrogen fuel, and liquefied natural gas-powered heavy trucks; deploying photovoltaic power generation and energy storage facilities reasonably in transportation hub stations and along the highway, and taking specific measures such as charging piles, supporting power grids, filling (gas) stations, hydrogen refueling stations and other infrastructure construction orderly.
2.2.4. Promoting scientific and technological innovation
The key point of this policy is to clarify the mechanism of highway transportation and energy conservation and emission reduction, breaking through the key technologies of green and low-carbon transportation, and taping the greater potential of energy conservation and emission reduction through technological innovation, promotion and application. Policy priorities include deepening basic theoretical research on comprehensive prevention and control of traffic pollution, developing new technologies such as monitoring and supervision of traffic energy consumption and pollution emissions; accelerating the promotion and application of key technologies for energy conservation and environmental protection, and strengthening the research and development of new energy transportation equipment, facilities and equipment, hydrogen fuel-powered vehicles, green building materials and processes and other new equipment; improving the system of green transportation standards and specifications, and strengthening the formulation and revision of standards and specifications, such as access standards for energy conservation and carbon reduction, green operation specifications, and pollution emission limit standards.
2.2.5. Improving the monitoring system
The key point of this policy is to improve the carbon emission monitoring system and control policy, to make up for the gaps in the field of carbon emission measurement, and form a closed loop of carbon emission management in road transportation. Policy priorities include strengthening the basic carbon emission statistics and accounting, studying and formulating carbon emission statistics methods and accounting rules in the field of transportation; strengthening the incentive and restraint mechanism for green and lowcarbon transportation, and improving new governance measures such as credit transportation, carbon credits, energy contract management, carbon emissions verification, and green finance by category; using online monitoring system and big data technology to establish transportation carbon emission monitoring platform system; promoting the construction of near-zero carbon transportation demonstration areas and other specific measures.
3. Countermeasures for China's Road Transportation Carbon Reduction
Learning lessons from the typical practices and development experience at home and abroad, it is suggested that top-level scheme design and work measures could be implemented from three major areas of strategical carbon reduction initiative, technical carbon reduction initiative and management carbon reduction initiative, so as to achieve “carbon emission peak” and “carbon emission neutral” in China's road transportation as soon as possible.
3.1 Implement strategic carbon reduction initiative
The strategic carbon reduction initiative mainly aims at the top-level strategy of road transportation carbon reduction, and proposes the overall strategic layout, policy system and standard planning. The specific measures mainly include: formulating the measurement methods and standard specifications of road transportation carbon emissions, forming a clear and transparent emission data and indicator system, and defining the total amount and current composition of road transportation carbon emissions in the benchmark scenario and year; developing “The 2030·2060 Action Roadmap for Road Transportation Industry”, which focuses on carbon intensity control and supplemented by carbon emission total amount control, defined the main areas, ways to achieve and phased objectives of road transportation carbon reduction, and further consolidated consensus and joint efforts on carbon reduction; promoting the transformation of transportation mode to railway and inland river, improving the operational efficiency of multimodal transportation through facilities specialization, equipment modularization, service facilitation, data standardization, etc., to realize the transfer of road transportation to a cleaner transportation mode; deepening experience exchanges with EU countries in the field of transportation carbon reduction, and deepening cooperation in transportation carbon emission pricing and trading systems, carbon emission standards mutual recognition and data sharing, cross-border infrastructure connectivity, joint construction of zero carbon airports and seaports, and clean energy regional alliances.
3.2 Implement technical carbon reduction initiative
The technical carbon reduction initiative mainly aims at technical progress and scientific and technological innovation, and proposes new technologies, methods and models for road transportation carbon emission reduction. The specific measures mainly include: establishing statistical monitoring platform for road transportation carbon emissions; using Big Data, the Internet of Things, Blockchain and other digital technologies to achieve refined management of carbon emissions by means of enterprises and regions; increasing investment in clean energy, improving the construction of clean energy infrastructure in important transportation corridors and nodes, and accelerating the promotion of new energy vehicles such as electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen vehicles; vigorously exploring carbon reduction space of new transportation technologies, such as automatic driving, formation driving, photovoltaic pavement, electrified roads, underground logistics, and travel as a service (MaaS). For example, truck formation driving can reduce carbon emissions by about 10%~15%.
3.3 Implement managerial carbon reduction initiative
Managerial carbon reduction initiative mainly aims to improve the management system and governance capacity, by proposing a reward and punishment mechanism system for road transportation reduction. The specific measures mainly include: establishing a low-carbon traffic certification system, improving relevant standards and certification processes; implementing the “one ballot veto for high carbon emissions” mechanism, only transportation enterprises that have passed the low-carbon certification can apply for the relevant preferential policies of the transportation sector; innovating the green transportation financing system, and increasing investment in green transportation infrastructure by issuing green transportation bonds, reducing the capital of green transportation projects, and extending the service life of operating projects; carrying out zero carbon transportation capacity building, organizing large transportation and logistics enterprises to form a zero carbon alliance, launching carbon reduction initiatives, and widely carrying out training, technical exchanges, concept promotion and other capacity building work; promoting the transportation carbon emission trading system, implementing carbon emission pricing, emission charging, carbon reduction subsidies and other measures in accordance with the principle of “polluter pays”, establishing zero emission regions, and improving the transportation carbon emission trading market.
Reference
1.Our World in Data. Global CO2 emissions from fossil fuels. https://ourworldindata.org/co2-emissions
2.Pierre Friedlingstein et al. Global Carbon Budget 2022, Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 14, 4811–4900, https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-14-4811-2022, 2022.
3.Jingyi Zhen. How to Be a Pioneer in Transportation Under the Goal of “Double Carbon [N] China Economic Herald, 2022-07-02(002). DOI:10.28095/n.cnki.ncjjd.2022.000925.
4.Huapu Lu, Haixia Feng. Analysis and Thinking on Carbon Neutralization in Transportation Field [ J] Economic Guide to Sustainable Development, 2022 (Z1): 63-67.
5.Lichen Huang, Qiaosong Cao. Analysis of Green Development Countermeasures in the Transportation Field under the Carbon Neutral Target [ J]. Urban Transportation, 2021, 19(05):36-42. DOI:10.13813/j.cn11-5141/u.2021.0503.
6.Di Han. Reports Series On “Double Carbon Action” in The Industry: Observation On The Strength Of Green And Low Carbon Action In The Transportation Field Of Provinces During The “Fourteenth Five Year Plan” Period [R]. Beijing: Innovative Green Development Center, 2022.
来源:《中国公路》
作者:林坦

